Apple’s iOS operating system has improved considerably since its original release in 2007. Every new edition has introduced new technology and enhancements over the years. iPhone OS 2 brought the App Store, while iOS 14 incorporated 5G connectivity and iOS 18 introduced AI features.

In this editorial, we will revisit history and discuss different versions of iOS, from the initial iPhone OS to the recently launched iOS 18. You will learn about the major specifics of various versions and the turning points in the evolution of the iOS operating system.
iOS 18 – September 16, 2024

Apple gave iPhone users a preview of iOS 18 at WWDC 2024 and officially launched on September 16, 2024, along with the iPhone 16 series. This major update significantly boosts personalization options across the system and apps. You can customize the Home Screen layout and change the app icon theme.
Additionally, the Control center can be customized to accommodate new quick controls. For advanced privacy, iOS 18 lets users lock apps and choose which app can access which contacts.
The native apps, especially the Photos, Notes, and Mail apps, also received a major overhaul. Further, the company introduced a powerful AI-powered feature called Apple Intelligence. Last but not least, the iOS 18 Accessibility features make it easier to navigate the iPhone.
Key features of iOS 18
- Apple Intelligence features such as Genmoji, Math Notes, etc.
- Call recording
- Customizable Home Screen
- Redesigned Control Center
- New controls on the Lock Screen
- Lock and hide apps
- A new Passwords app
- Collections and Clean Up tool in the Photos app
- iPhone Game mode
- Text effects in Messages
- New emojis in Tapback
- Schedule messages with Send Later
- Messages via Satellite
- Categories in the Mail app
- Highlights in Safari
- Redesigned Reader in Safari
- Calculator history
- Download topographic maps
- Tap to Cash in the Wallet app
- Live audio transcription in Notes
- Integrated Reminders in Calendar
- Enhanced Journal app
iOS 17 – September 18, 2023

iOS 17 is announced on June WWDC 2023. The focus of iOS 17 was redesigning and upgrading the system apps and features. The Message, FaceTime, and Phone apps have several enhancements. Besides, Apple worked on connectivity by introducing NameDrop and FaceTime on Apple TV.
The most highlighted features of iOS 17:
- Personalized Contact Posters
- Live Voicemail
- Video voicemail and Reactions on FaceTime
- Search Filter, Catch up arrow, Swipe to reply, Transcription of voice messages, Check-in features in Messages app
- Live Stickers
- StandBy feature
- Share contact card using NameDrop
- Journal app
- The mindfulness feature on the Health app
- Create Profiles on Safari
- Collaborated playlist on CarPlay
- Upgraded Autocorrect and Dictation abilities
iOS 16 – September 12, 2022
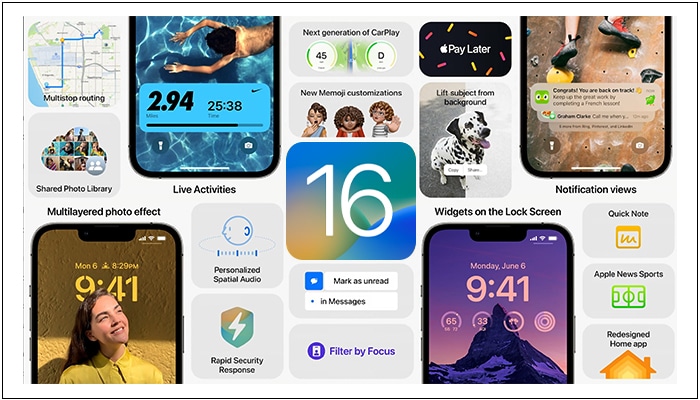
iOS 16 was announced at the WWDC event in June 2022 and released in September 2022.
The most noticeable upgrade in iOS 16 was the supported features for Dynamic Island for iPhone 14 Pro models. It made the new notch design more fun by displaying animated notifications and offering controls around the camera.
Also, Crash Detection, Always-on display, Emergency SOS via Satellite, and other exclusive features of the iPhone 14 series supported with iOS 16.
- Customizable Lock Screen
- Live Activities
- Better Focus Filters
- New Message features
- Redesigned Apple Maps
- Apple Pay Later
- Apple Order Tracking
- iCloud Shared Photo Library
- Live Texts on videos
- Passkeys
- Safety Check function
- Improvements to Spatial Audio
- Voice Isolation in phone calls
- Advanced Data Protection for iCloud
- Apple Music Sing karaoke
iOS 15 – September 24, 2021
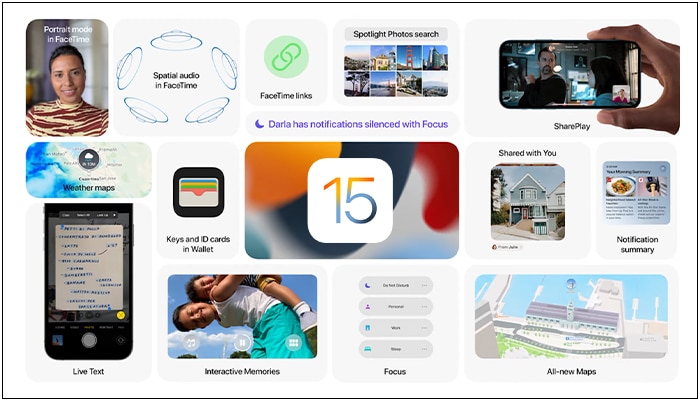
Unlike iOS 16, the iOS 15 update was more focused on software bug fixes, system improvements, and polishing features of built-in apps.
Additionally, the pandemic era influenced the feature upgrades. Apple worked on increasing security and privacy, preventing ad tracking, and improving Siri, Camera, FaceTime, Messages, etc.
As of writing, iOS 15 is supported on the iPhone 6S series and later and the iPod touch 7 Gen.
- New FaceTime features – Spatial audio, SharePlay, FaceTime Link, Mic modes, Portrait modes, etc.
- iMessage Share with you
- Better Focus Filters with Notification Summary, Signal your status, etc.
- Live Text and Memory features in the Photos app
- Advanced Spotlight search
- App Privacy Report
- Mail Privacy Protection
- On-device Siri
- Digital Legacy program
- Redesigned Safari tabs
- Detailed Maps
- Improved Health and Wallet app
iOS 14 – September 17, 2020

iOS 14 version lists similar system improvements very much like iOS 15. There were no significant changes. Apple added a few enhancements like privacy controls, Home Screen widgets, customization options, etc.
Key features of iOS 14:
- Widgets on the Home Screen
- App Library
- Improved call notifications
- Picture in Picture Mode
- Redesigned Siri
- Translation, Password monitoring, and Website Privacy Report in Safari
- Pinned Conversations and improved group texting in Messages
- New Memoji Styles and Stickers
- Cycling directions and Electric vehicle routing in Maps
- Translate app
- App Clips
iOS 13 – September 19, 2019
Before iOS 13, iPad also ran iOS. But Apple took a big step by introducing a new iPadOS to make the iPad more productive and a possible laptop replacement. Since then, iOS and iPad OS have always been rolled out simultaneously.
The most visible new feature was the Dark Mode. Additionally, iOS 13 improved essential functions, like faster app start, Face ID, Portrait Lightning, and redesigned pre-installed apps.
Key features of iOS 13:
- System-wide Dark Mode
- 30% faster Face ID unlocking
- Revamped Apple Maps
- Smarter HomeKit
- Sign In With Apple user account
- New privacy and security options
- Portrait Lighting effects
- New, improved Siri voice
- Overhauled system apps like Photos, Mail, Reminders, and Notes
iOS 12 – September 17, 2018
The 12th iteration of the iPhone software had just a few new additions. Primarily, it improved regularly used functionality for providing a better user experience. Apple introduced Siri Shortcuts, ARKit 2, Screen Time tracking, etc.
Key features of iOS 12:
- Grouped Notifications
- Screen Time
- ARKit 2 for enhanced Augmented Reality
- Siri improvements
- Memoji
iOS 11 – September 19, 2017
iOS 11 has special features to support the iPod touch, iPad, Apple Watch, and Apple TV.
Therefore, its primary features included more iPad-specific features like split-screen apps, drag-and-drop functionality, a file browser app, and support for Apple Pencil handwriting, etc.
Key features of iOS 11:
- iPad functions
- AirPlay 2
- Support for Augmented Reality
iOS 10 – September 13, 2016
The release of iOS 10 was a watershed moment for the Apple ecosystem. It offered several APIs to integrate third-party solutions into the system apps. Thus, the iPhone got a boost of interoperability and customization in its UI and applications. Also, Siri became more accessible to third-party apps. The best part was Apple allowed users to uninstall built-in apps.
Key features of iOS 10:
- Embedded iMessage apps
- Delete built-in apps
- Split Control Center into multiple panels
- Integration of Siri with third-party apps
- Smarter QuickType keyboard
- 3D touch displayed widgets
iOS 9 – September 16, 2015
iOS 9 prioritized building a solid base for the operating system to improve the speed, responsiveness, stability, and performance of older devices. After significant modifications to iOS’s design and technological base, users started to feel that iOS was no longer the reliable, trustworthy, and competent it previously was.
So, Apple decided to work on strengthening the OS’s basis rather than introducing new features, laying the framework for the larger enhancements in the next iOS updates. To get a public reaction and acceptance, iOS got the Public Beta feature. So, before the actual release of the upcoming iOS version update, people can get a taste of it.
Key features of iOS 9:
- Night Shift
- Low Power Mode
- Public beta program
iOS 8 – September 17, 2014
In iOS history, iOS 8 was a significant update as it introduced the contactless payment system Apple Pay and the Apple Music subscription service. It also polished the iCloud features for more reliable and consistent performance. The most useful feature unveiled was the Handoff feature to seamlessly switch between Apple devices.
Apple walked in with a Dropbox-like iCloud Drive and the addition of an iCloud Picture Library and an iCloud Music Library. To save subscription costs, Apple offered Family Sharing, which allows users to enjoy content individually with a single subscription. Moreover, the HealthKit and HomeKit features focused on users’ daily lives.
Key features of iOS 8:
- Apple Music
- Apple Pay
- iCloud Drive
- Handoff
- Family Sharing
- Spotlight Suggestions
- QuickType in keyboard
- HomeKit and HealthKit
- Extensibility framework for third-party extensions
iOS 7 – September 18, 2013
iOS 7 was a troublesome update, and users were dissatisfied as things didn’t operate as expected. It included a significant redesign of the user interface in the update and opted for a flat look. But some users found it difficult to read because of the tiny, thin letters, and others experienced motion sickness because of the constant animations.
Besides, Apple provided quick access to the most used features with Control Center and launched AirDrop, Activation Lock, and CarPlay. Additionally, Siri got new voices and a redesigned look.
Key features of iOS 8:
- Activation Lock
- AirDrop
- CarPlay
- Control Center
- Thumbnails in App Switcher
- Improved Notification Center
- Smarter Siri
- Touch ID
iOS 6 – September 19, 2012
In the history of iOS versions, iOS version 6 saw the most controversies because of Apple’s escalating rivalry with Google. Although the newly launched Siri was a real breakthrough technology, issues with it resulted in significant revisions.
Besides, from iPhone OS version 1.0, Google has included the Maps and YouTube applications pre-installed. But this time, Apple replaced Google Maps with a new Apple Maps. It was not up to the mark because of glitches, inaccurate instructions, and issues with other functionalities.
Sidelining the flaws, iOS 6 has a Podcast app, a more capable Siri, a Panoramic mode in the Camera, and access to make FaceTime calls over cellular data.
Key features of iOS 6:
- Apple Maps
- Do Not Disturb
- Passbook (now Wallet)
- New features in Siri like launching apps
- Panoramic photos
- FaceTime over cellular data
iOS 5 – October 12, 2011
iOS 5 was a turning point for Apple as it introduced crucial new features like Siri, iCloud, wireless iPhone activation, and Wi-Fi iTunes syncing. Users could download and install software updates on their iPhones without a computer. Besides, for better user experience and accessibility, iPhone got Notification Center and iMessage.
Key features of iOS 5:
- Siri
- iCloud
- iMessage
- Notification Center
- Redesigned Reminders and Newsstand apps
- Wireless syncing and activation
iOS 4 – June 22, 2010
With iOS 4, the futuristic iOS started to take form as Apple tagged the “iPhone OS” as “iOS” for the first time. Many revisions to this version included features like FaceTime, multitasking, iBooks, Game Center, arranging programs into folders, custom wallpapers, Personal Hotspot, AirPlay, and AirPrint.
Moreover, Apple included Bing as a search engine for Safari and allowed users to merge multiple email accounts in one inbox. It was the first iteration of iOS to stop supporting all iOS devices. It was incompatible with the first-generation iPod touch or the iPhone.
Key features of iOS 4:
- FaceTime
- Multitasking
- AirPlay
- AirPrint
- iBooks
- Game Center
- Personal Hotspot
- System-wide spell checking
- 5x digital zoom
iPhone OS 3 (iOS 3) – June 17, 2009
iOS 3 was the first operating system for the iPad and came out of the box with the iPhone 3GS without any charge. Users were able to copy and paste text system-wide. Besides, Spotlight search, MMS support in the Messages app, and the capability to shoot films using the Camera app are just a few of the new features it included.
Key features of iOS 3;
- Copy and paste
- Spotlight search
- Voice Memo app
- Recording videos
iPhone OS 2 (iOS 2) – July 11, 2008
iPhone OS 2 was meant for the iPhone 3G model, which included support for the 3G network. As the iPhone became a big hit, app developers tried to jailbreak the iPhone to install third-party apps. So, Apple introduced development tools like APIs and SDKs for software companies to launch apps in the App Store to prevent installing apps from the web.
The App Store had around 500 applications when it debuted. Podcast support, walking and public transportation instructions in Maps, an iTunes Genuine playlist, and enhancements to Mail, Calculator, and Contacts using Microsoft Exchange support were other significant additions to iPhone OS 2.
Key features of iOS 2:
- App Store
- Developer APIs and SDKs
- Support for Microsoft ActiveSync and Microsoft Exchange
- Improved Maps app
iPhone OS 1 (iOS 1) – June 29, 2007
iOS debuted with the first iPhone in June 2007. Nevertheless, it was mostly powered by OS X, the Mac software. It had core iOS UI, iTunes integration, Multi-touch gestures, Mobile Safari, iPod, Visual Voicemail, and Maps, which emerged as advanced smartphones at that time.
However, it lacked support for actual third-party applications and came with basic pre-installed apps like Calendar, Pictures, Camera, Notes, Mail, and Phone.
Key features of iOS 1:
- Visual Voicemail
- Multitouch interface
- Calculator
- Calendar
- Camera
- Clock
- iPod
- iTunes
- Maps
- Music (iPod Touch)
- Notes
- Phone
- Photos
- Safari
- Settings
- Stocks
- Text
- Videos (iPod Touch)
- Weather
- YouTube
Long live iOS!
Apple’s iOS has evolved significantly over the years, from its humble beginnings in iPhone OS 1 to the latest iOS 18. All the new features and improvements have revolutionized how iPhone users use their phones and have consistently stretched the limits of what mobile technology can do.
iOS users can expect more good things in the future because Apple is not stopping at anything in developing their devices. Let us anticipate the following chapter of the Apple iOS journey and be surprised by the remarkable advancements in the iPhone experience.
Explore more…

