When it comes to protecting your online privacy, choosing between Apple’s iCloud Private Relay and VPN can be confusing. When you enable iCloud Private Relay, it hides your IP address and secures the information you send on the internet. That sounds exactly like the function of a VPN, right? But let me tell you, both are quite different!

In this article, I will break down the basics and share a detailed comparison of iCloud Private Relay vs. VPN. So, you can decide which one might be right for your iPhone, iPad, or Mac.
Since this is a detailed discussion, if you need a quick link to a desired section, you can just select it from the table below!
What is iCloud Private Relay?
You can use the iCloud Private Relay feature on Safari across your Apple devices if you have an iCloud+ subscription. While browsing, this feature encrypts your data, such as your location, IP address, and DNS requests.
To accomplish this, all your internet interactions are routed through two separate servers. Thus, websites, online trackers, even Apple, and your internet service provider can’t trace your identity and browsing activity. In return, you will not be served annoying, targeted ads.
Curious how so much happens while your searched website loads in seconds? Keep reading!
How does iCloud Private Relay work
After you set up iCloud Private Relay on your Apple ID, all your web browsing requests on Safari are sent through two internet servers. As the name suggests, it’s like a relay race. Let me explain with an example.
Suppose you searched for iGeeksBlog on Safari. Now, Safari sends your DNS request to Apple’s server.
In this first relay, Apple encrypts the web address you searched for from your ISP. So, Apple and your network provider only know your device’s IP address, not your browsing activity.
In my case, both parties know I am searching for something on Safari but can’t detect that I want to visit iGeeksBlog.
In the next relay, your web request goes to third-party content providers through a secured link. They give you a proxy IP address, hiding your real one. Then, the server deciphers the encrypted DNS record and navigates you to the requested website from the new IP address.
Therefore, the third-party servers and the website’s trackers only know I want to visit iGeeksBlog without my identity.
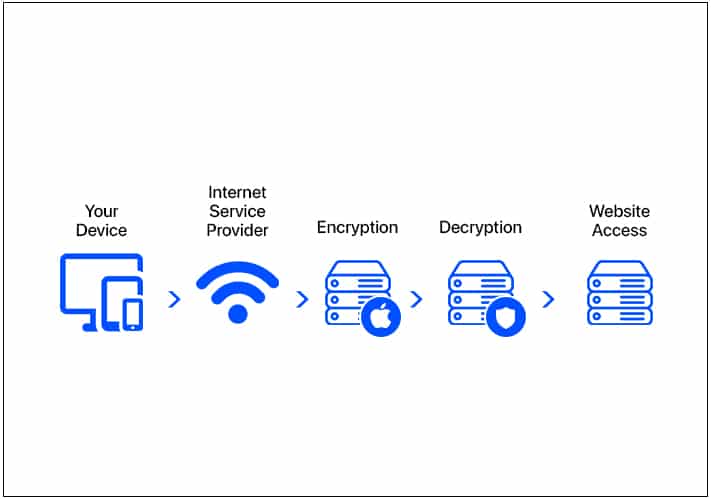
Altogether, neither Apple and ISP nor third-party servers and websites can track down your device’s location, your demographics, or what you do on the internet.
Now that you understand the functionalities of iCloud Private Relay, let’s explore the advantages and limitations you’ll get when using this!
Pros and Cons of using iCloud Private Relay
You may want to use iCloud Private Relay if you want:
- Enhanced privacy for free. When you pay for iCloud+, Private Relay is a bonus.
- Super easy set up process. You don’t need to download anything or configure your device. Simply, toggle on Private Relay from iCloud settings.
- No extra hassle to use Private Relay on other Apple devices. Once you enable the feature, all your Apple devices logged in with the iCloud account can access it.
However, there are some concerns you must know before committing yourself to Private Relay.
- It’s obvious that only Apple users can take advantage of this. However, the feature only works in the Safari browser and no other browsers on your iPhone or Mac.
- Some websites may not load fully due to the relay. Also, due to the masked identity, few regions and websites restrict its usage.
- Despite the encryptions, Apple still logs very little user data. However, they claim this data will not be used to identify users.
So, overall iCloud Private Relay offers robust privacy. However, if you want to have a more customized experience and advanced security features, you may consider getting a VPN. In the next section, I will explain the features and functionalities of a VPN.
What is a VPN?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, lends you a temporary IP address and encrypts all your internet activities. It routes your traffic through a remote server than your ISP’s. Thus, you can enjoy a secure connection to the internet without risking your privacy.
Sending your DNS requests through servers? Hmm, sounds a bit like Private Relay, isn’t it? But, in truth, there’s more to it. Let me explain how it work.
How does a VPN work?
Before you go online, you must enable VPN on your device and connect to a remote server. It will hide your actual device’s location and assign you a new IP address. Now, when you search anything on browser, your DNS request goes to the VPN server first.
There, your data is encrypted and sent to the requested website through the proxy IP address. So, your ISP and other third-party trackers won’t detect your real identity and location. They will see your location the same as your connected VPN server.
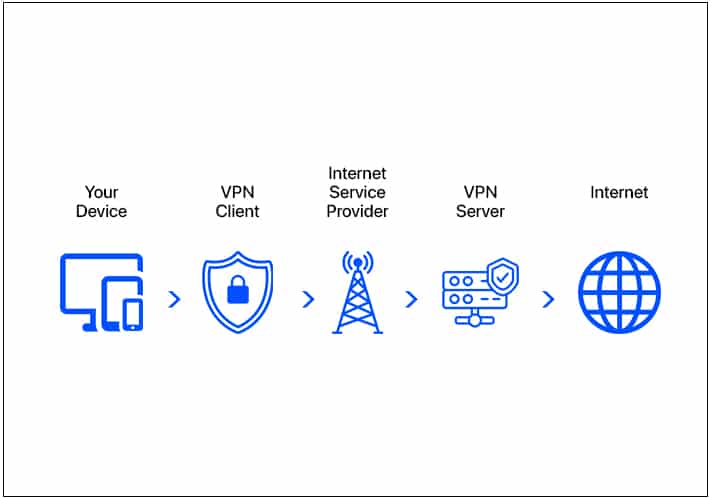
Note: These are the basics of any VPN service. Advanced VPN services, such as SurfShark, offer high-end encryption, no-logs policy, industry-leading connection protocols, DNS leak protection, and much more.
Pros and Cons of using VPN
VPN can be your go-to privacy tool because:
- VPN works on all operating systems and web browsers. If you are using a premium service, you only need to log in to the devices with your credentials.
- Besides browser activity, all your internet interactions through apps and games are also protected. This is useful when connected to public Wi-Fi or shared networks.
- Advanced AES-256 encryption provides enhanced security and data encryption. So, even hackers can’t snap your privacy.
- As the remote servers are located across the world, you may access geo-restricted contents.
- VPN prohibits you from accessing malicious websites.
Despite so much to offer, VPN also has some disadvantages:
- When surfing the internet via VPN, you may experience lags. Your internet speed may decrease depending on the distance and traffic of your connected server.
- Your DNS requests are processed through third-party servers. So, few free VPN services may monitor and sell your online activity.
- Setting up VPN on your device may have a learning curve.
I hope now you have a clear understanding of VPN service. You may find iCloud Private Relay is a simplified version of a VPN. But that’s not the case.
Is iCloud Private Relay a VPN?
The simple answer is NO. At first glance, I thought iCloud Private Relay and VPN are the same thing. But after using both, I understood they operate differently and can’t be used as substitutes.
So, what’s different? Let’s understand in detail!
iCloud Private Relay vs VPN – Key differences
iCloud Private Relay only protects your Safari web traffic. This means that your other internet browsing sessions are not safe. A VPN, on the other hand, secures all your online activities, no matter what browser or device you use.
Though iCloud Private Relay hides your IP address and requested website data, Apple can still see your real IP address. VPN masks both your IP address and your online traffic. So, all data going to and from your device is safe and secure.
The most distinguished difference is Apple provides a proxy IP address of a server from your region. However, VPN service lets you pick a specific country’s server.
Overall, iCloud Private Relay focuses on hiding browsing activity, while a VPN secures your entire internet connection with additional security features.
What should you prefer – iCloud Private Relay or VPN?
The choice between iCloud Private Relay and VPN depends on your specific needs. If you value seamless integration with Apple devices, use Safari most of the time, and prioritize browsing privacy, iCloud Private Relay may be the way to go.
However, if you seek broader device compatibility and comprehensive internet security, a VPN might better suit your requirements.
As I constantly surf the internet to research content, I personally use a VPN on my Mac. It saves me from trackers, marketers, malware, and hackers, keeping my browsing experience clean and safe.
Signing off…
That’s all for the iCloud Private Relay vs. VPN war. Ultimately, the decision between iCloud Private Relay and VPN comes down to your priorities. Consider your device ecosystem, privacy concerns, and internet usage habits to determine which option aligns best with your needs.
Read more:
